SISO stands for Single Input Single Output
In a SISO system a single antenna is used for transmission and reception. SISO is typically used in radio, satellite, GSM and CDMA systems.
SISO datalink
SISO stands for Single Input Single Output
In a SISO system a single antenna is used for transmission and reception. SISO is typically used in radio, satellite, GSM and CDMA systems.
SISO datalink

The antennas perform the activity of both transmitting and receiving the signal in order to establish the datalink. A typical MANET SISO datalink will achieve a throughput in the region of about 20Mbps. The legacy Wave Relay® MPU4 radio is an example of a SISO radio.
MIMO stands for Multiple Input Multiple Output.
The Wave Relay® MPU5 is a next generation MIMO radio.
In a MIMO system, multiple antennas are used for transmission and reception. MIMO systems achieve much higher data rates because of a technique used to transmit data simultaneously across multiple antenna. This technique is called spatial multiplexing.
MIMO datalink
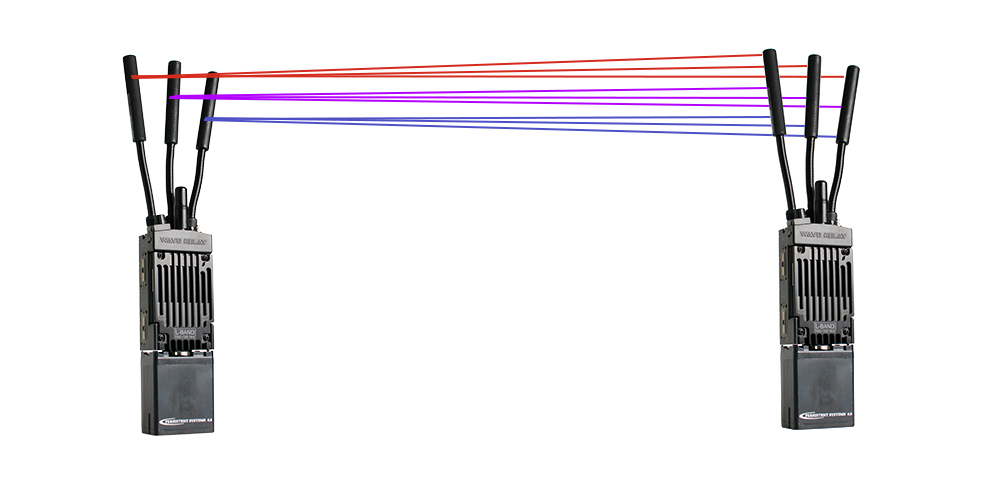
The use of multiple antennas in a MIMO system provides other benefits. The ability to make use of multiple antennas, each one at a slight angle, provides increased performance and resilience – this is commonly referred to as antenna diversity.
Antenna diversity benefits your datalink by effectively giving the antenna a different “viewpoint” to its peers. Where antenna 1 might be susceptible to interference because of its angle (polarisation), antenna 2 and 3 might not be as influenced by interference because of their slightly different polarisation.
To help explain, a good analogy of antenna diversity is like looking at the same geographical landmark from 3 different angles – you might see more of the landmark at slightly differing perspectives.
Another technique employed in MIMO technology is space-time block coding (STBC).
Space–time block coding works in conjunction with spatial multiplexing, and is a MIMO technique used to transmit multiple copies of the same data across the three antennas and to exploit the various received versions of the data to improve the reliability of the data transfer.
Data transmitted via radio waves between two points has a particularly difficult journey. Every time a radio signal encounters a building, a wall or other obstacle, the RF signal basically inverts and fades. When using a 360° omni-directional antenna, this happens a lot!
These constant reflections and refractions of the RF signal are a form of interference. Each bounce of the signal reduces its overall clarity. Sending the same data three times (once per antenna) means that some copies of the received data may be closer to the original than others.
This redundancy results in a higher chance of being able to use one or more of the received copies to correctly decode the received signal. Space–time coding combines all the copies of the received signal in an optimal way to extract as much information from each of them as possible.
The Wave Relay® MPU5 radio uses these MIMO techniques to provide the most efficient, most advanced MANET system currently available.
The advantages of a MIMO datalink over a SISO datalink include:
• Increased throughput: Wave Relay® MIMO offers speeds of over 120Mbps (5 times faster than SISO) for multiple streams of multicast HD video, 32+ voice talk groups, and data.
• Increased range: Wave Relay® MIMO is less susceptible to interference, and therefore has a better signal to noise ratio. This effectively means that the signal can travel further.
• Increased coverage: 360° coverage of high-throughput, long distance data
• Redundancy: Wave Relay® MIMO has three antennas and uses a combination of spatial multiplexing, space-time block coding and antenna diversity techniques to ensure the signal has the best possible chance of reaching its destination.
• Resilience: Less chance of interference means a more reliable link
• Improved overall performance: 5 x the throughput and 4 x the range of SISO systems
Want to hear more about insights, product updates and industry trends? Sign up to our newsletter to stay informed: